Sexually Transmitted Infections – Sexually transmitted infections can cause sexually transmitted diseases. Your diagnosis may determine your treatment options. The disturbing reality is that According to WHO, more than 1 million treatable sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) are acquired every day in persons aged 15 to 49 worldwide, with the majority of them asymptomatic. Let’s explore STI prevention, diagnosis, test and treatment through this article.
Table of Contents
What is Sexually Transmitted Infections?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are the origin of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). They are distributed mostly through sexual contact. Bacteria, viruses, & parasites are all responsible for STIs or STDs. A sexually transmitted disease can spread from person to person by blood, sperm, vaginal, and other body fluids.

Sexually transmitted infections can spread in methods other than sexual contact. For example, STIs can be transmitted to infants during pregnancy or delivery. STIs can also be transmitted through blood transfusions or sharing needles. STIs do not usually produce symptoms. A person may get a STI or sexually transmitted disease from someone who looks in good health & may be unaware that he/she has an infection.
Read the first part of Sexually Transmitted Infections STI by click on the below link:
Sexually Transmitted Infections STI: 11 Common Types, Causes, Symptoms, and How to Minimize Your Risk
What are the complications of STI Sexually Transmitted Infections?
If you are not worried about the treatment of sexually transmitted infections, you may face lifelong complications. Following are some of the common complications of untreated STIs.
- HIV: It can lead to AIDS
- Syphilis: It may infect a developing fetus and harm your nervous system as well as organs.
- Spreading STIs: There is a risk that you will spread STIs to your sexual partners.
Women or people assigned female at birth (AFAB) may experience the following STI complications:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): It may damage your uterus and make you infertile.
- Infertility
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Ectopic pregnancy
Untreated STIs in men or those who were assigned male at birth (AMAB) can result in:
- Swollen, sore testicles
- Infections in the urethra and prostate
- Infertility
Read Also: Premature Ejaculation – Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
Sexually Transmitted Infections Prevention
The only 100% guaranteed method of preventing STIs is to never engage in sexual activity. However, there are steps you may take to lower your chance of getting a STI and its complications:
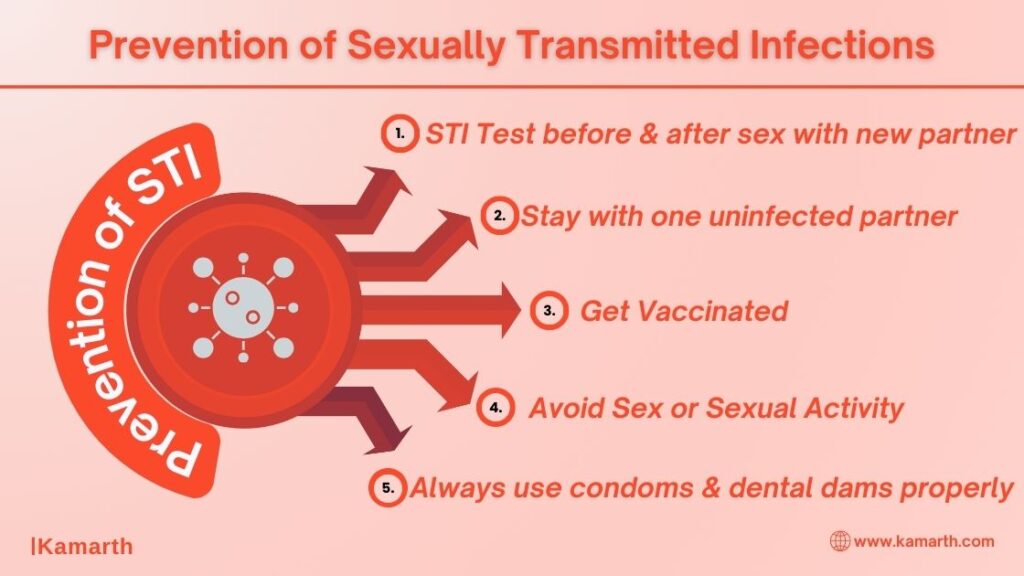
- Avoid Sex or Sexual Activity: Not having sex is the best method to prevent STDs.
- Stay with one uninfected partner: One strategy to prevent an STD is to remain in a committed relationship where both partners have sex only with each other and make sure that neither partner is infected.
- Wait and Test: Wait to engage in sexual activities with new partners or have vaginal or anal sex until you have both undergone testing for STDs. Oral Sex might be less dangerous. However, if a person does not wear a dental dam or a condom (latex or polyurethane), STIs can still transmit from one to another. The genital and oral mucous membranes cannot come into contact with one another due to the barriers such as male condoms.
- Get Vaccinated: Certain STDs can be avoided by receiving a vaccination prior to engaging in sexual activity. Hepatitis A and B, as well as the human papillomavirus (HPV), are the causes of STDs that can be prevented with vaccination.
- Always use condoms and dental dams properly: Don’t forget to use a fresh latex or polyurethane condom or dental dam for every sex whether it be oral, vaginal, or anal, use. Never use a latex condom or dental dam with an oil-based lubricant, like petroleum jelly. Moreover, less protection is provided by these kinds of barriers against STDs like HPV and herpes that involve open genital sores. Keep in mind that Intrauterine devices (IUDs) and birth control pills are examples of non-barrier modes of contraception that do not offer STI protection.
- Male circumcision: Research indicates that circumcision can reduce a man’s chance of contracting HIV from an HIV-positive woman by up to 60%. Additionally, male circumcision may help stop the spread of genital herpes & HPV.
Read Also: Morning Erection – What you need to know about Morning Wood
STI Diagnosis and Tests
A doctor or other healthcare expert can do tests and examinations to determine if you have a STI or another illness. There is a different test for different STI or STD. You will discuss the test(s) you require with your provider. STI testing could consist of:
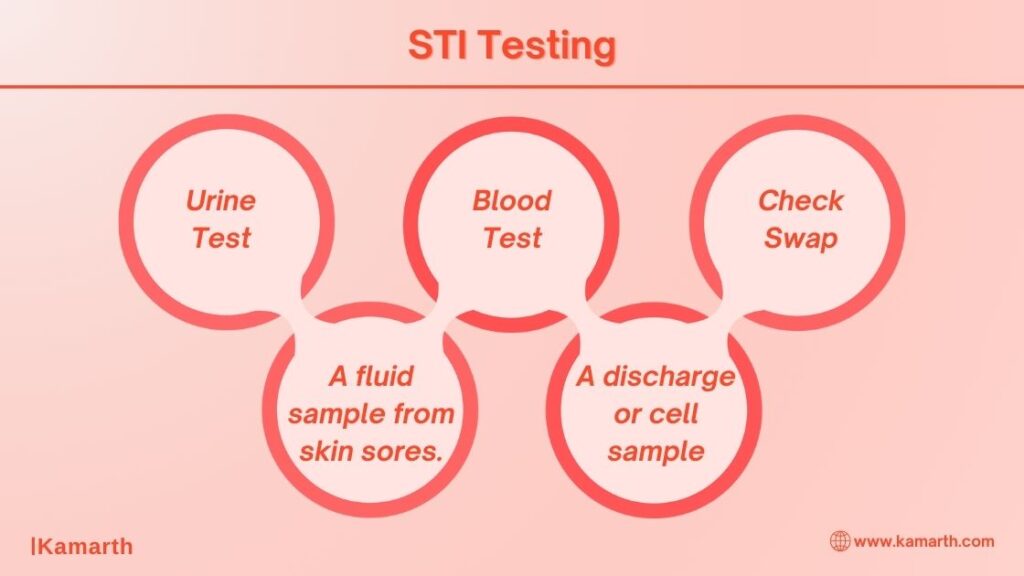
- Urine test
- Blood test
- Cheek swab
- A fluid sample from skin sores.
- A discharge or cell sample from the body part such as vagina, urethra, cervix, penis, anus or throat.
Most STI tests don’t hurt. A blood test may cause a tiny squeeze, or a swab contacting a lesion may cause a sting.
Read Also: Erectile Dysfunction – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Management and Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections
Certain STIs can be treated by doctors:
- Antibiotics can treat trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
- Antibiotics can be used to treat gonorrhea. But some drug-resistant strains of the bacterium have surfaced; these strains are resistant to conventional therapies and might be more challenging to treat.
- Antibiotics can also be used to treat syphilis. Depending on the stage of syphilis, your clinician will select a different medicine.
- Treatment for acute hepatitis B is typically not necessary. Antiviral drugs are used to treat chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesn’t go away on its own.
Certain diseases are incurable, although therapies can help decrease symptoms. Herpes, HPV, & HIV come within this group.
- To treat herpes, specialists will prescribe antiviral drugs to shorten the outbreak. Some patients use these drugs on a regular basis to lessen the risk of an epidemic.
- Daily antivirals are also used to treat HIV by preventing the virus from multiplying in the body. Most patients will be virus-free after 6 months of therapy.
- Clinicians do not have particular therapies for HPV-caused genital warts. However, they may recommend topical drugs or undertake operations to help decrease or eradicate the lesions.
It’s important to keep in mind that STIs might re-occur even after treatment has been completed.
Read Also: Sperm Freezing: The Key to Unlocking Your Garden’s Potential
A note from Kamarth
Most STIs are treatable, if not curable. Prevention is vital, as is frequent screening to ensure that any infections are treated as soon as possible. If you have any symptoms, no matter how small, you should get medical assistance from a skilled healthcare expert. We advise you to go through an STI test if you or your partner have doubts regarding STD.
Some Additional Doubts
Question: How common are sexually transmitted infections?
Answer: Sexually transmitted diseases are frequent. Every year, around 3.74 billion STI occur worldwide.
Question: How often should I get tested for STIs?
Answer: Most of the doctors suggest yearly STI testing. If you have several sexual partners, you may want to get tested more frequently, perhaps every 3 to 6 months.
Question: What is expedited partner therapy?
Answer: When you are diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea, your healthcare professional may prescribe expedited partner treatment (EPT) without first evaluating your partner.
Question: What if I have an STI and I’m pregnant?
Answer: If you are pregnant and have an STI, contact your healthcare professional straight away. They will discuss treatment choices to ensure the safety of both you and the fetus.
Question: Can I get a STI by open-mouth kissing?
Answer: Open-mouth kissing is regarded as a low-risk action for the transmission of STIs, including HIV. However, prolonged open-mouth kissing may cause skin injury around the mouth & lips. This would allow HIV to spread from an infected individual to their partner. Because of this danger, the CDC advises exercising caution while dealing with an infected partner.
Read More:-
Teenage Marriage – Cause, Implication, Why should it stop?
Emergency Contraceptive Pills – Unwanted 72, When to take
Is Breast Size Matter? – Is bigger best, types
POCSO Act – Feature, Propose, Safeguard, Background
Is Masturbation good or bad? – Benefits, Addiction, Disadvantage
Porn Addiction – Is it real?, Causes, Signs, Harmful, Beneficial
How do girls masturbate?
Do girls masturbate?
Understanding Miscarriage – Critical Prevention, 05 way to Diagnosis, and Effective Treatment
Reference Links:-
https://medlineplus.gov/sexuallytransmittedinfections.html
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295860493_Knowledge_about_sexually_transmitted_diseases_among_primary_health_care_providers
https://www.prevention.va.gov/docs/mens-health-guide/STIs.pdf
https://www.who.int/health-topics/sexually-transmitted-infections#tab=tab_1
https://www.epicentro.iss.it/ist/pdf/Suligoi%20IST%20CollanaRagazziPasteur%202020%20EN.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10178083
